Selecting the right crude pump is essential for efficiency. The crude oil industry is vast, with global production reaching about 95 million barrels per day. Each operation has unique requirements. A suitable pump can significantly influence productivity.
Consider the different types of crude pumps available. For instance, centrifugal pumps work well for high flow rates, while positive displacement pumps are more effective for high viscosity applications. Understanding your specific needs is crucial. Using the wrong pump can lead to inefficiencies and increased costs.
Also, think about maintenance needs. Regular upkeep is vital to ensure long-term operation. Neglecting maintenance can result in downtime and lost profits. Ultimately, making the right choice in a crude pump is a complex task. It requires careful consideration of many factors. It's worth reflecting on past decisions to improve future outcomes.

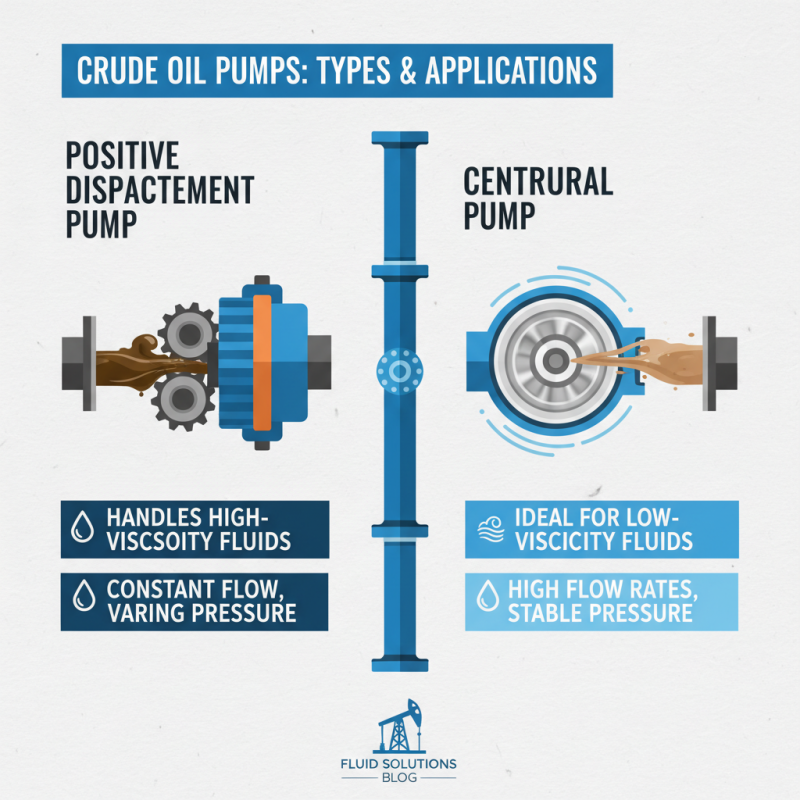
When choosing the right crude pump, it's crucial to understand the two main types: positive displacement and centrifugal pumps. Each type has its unique advantages and is suited for specific applications. Positive displacement pumps are known for their ability to handle high-viscosity fluids. They operate by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and forcing it through the discharge. This type is ideal for applications where consistent flow rates are essential, even under varying pressure conditions.
On the other hand, centrifugal pumps are more common in the industry due to their efficiency in handling low-viscosity fluids. They work by using rotational energy to impart velocity to the fluid, making them suitable for large-volume pumping. According to a report by the American Petroleum Institute, 65% of the crude transport system utilizes centrifugal pumps, highlighting their predominant use in the industry.
Tips: Consider the fluid's viscosity. If it's thicker, a positive displacement pump may suit your needs better. Assess system requirements carefully. Flow rate and pressure can drastically influence your choice. Understanding your specific application helps in selecting the best pump type. Taking the time to reflect on these factors can lead to a more efficient pumping solution.
Choosing the right crude pump involves understanding key factors like flow rate, pressure, and viscosity. Flow rate is crucial. It determines how much crude oil the pump can handle within a specific timeframe. According to industry reports, a flow rate of 500 to 1,500 gallons per minute is common for many applications. However, this depends on your particular needs. Too low a flow rate can lead to inefficiencies.
Pressure is another significant factor. The pump must generate enough pressure to transport crude oil through various systems. Ideal pressure ratings usually range from 50 to 200 psi. Inadequate pressure can result in pipeline degradation and costly repairs. It's essential to have accurate pressure data to avoid such issues.
Viscosity affects how easily the crude oil flows through the pump. Higher viscosity means the oil is thicker, which impacts the performance of the pump. Industry standards suggest adjusting the pump design according to viscosity measurements. If viscosity isn't considered, it could lead to unexpected downtime and maintenance challenges. Each of these factors requires careful evaluation. Proper analysis can directly influence efficiency and operational costs.
| Flow Rate (GPM) | Max Pressure (PSI) | Viscosity (cP) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 150 | 100 | Oil Transfer |
| 100 | 200 | 50 | Crude Delivery |
| 150 | 300 | 150 | Pipeline Injection |
| 75 | 100 | 200 | Heat Exchanger |
| 30 | 50 | 30 | Batch Processing |
Choosing the right crude pump involves careful consideration. Material compatibility is crucial. The pump's materials should resist corrosion and wear. Different fluids can react uniquely with various materials. This factor directly impacts pump longevity and efficiency.
For instance, if the fluid is abrasive, a durable material is needed. If it's corrosive, you may want stainless steel or certain plastics. Sometimes, people overlook this step. They focus more on pump size or flow rate. However, if the materials fail, the pump won’t last. The costs of replacement can be significant.
Testing materials in controlled conditions can be effective. Real-world conditions might differ. Manufacturers often provide guidelines, but they can't cover every situation. It's wise to gather feedback from users in similar environments. Understand their experiences with specific materials. This knowledge can guide you in making a more informed choice. Be prepared to re-evaluate your selections as conditions change. Adjustments may be necessary to ensure optimal performance.
When selecting a crude pump, efficiency is crucial. One vital metric is Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH). NPSH indicates if the pump can function properly without cavitating. Cavitation happens when the pressure of the liquid drops too low. This can damage the pump and reduce efficiency. Understanding the NPSH requirement of your pump is crucial. It tells you if the pump can handle the suction conditions.
Energy consumption is another key factor. A pump that uses a lot of energy may seem powerful, but it can lead to high operational costs. Look for pumps designed to optimize energy use. Small design features can make a big difference. For instance, impeller design affects both flow and energy use. Assessing these details can ensure that your crude pump meets both performance and cost-effectiveness.
Selecting the right pump isn't always straightforward. Many people overlook the importance of these metrics. Some assume all pumps perform the same. This can lead to poor choices. Take time to analyze your specific needs and conditions. A little research can save you significant time and money later. Consider all aspects carefully.
When choosing a crude pump, cost considerations are vital. Initial costs often grab attention first. However, long-term operational costs can overshadow that upfront price tag. Maintenance, energy efficiency, and downtime affect overall expenses. It’s important to evaluate these factors comprehensively.
Energy costs can accumulate quickly. A pump that uses more energy may seem cheaper initially, but that’s misleading. Consider operational efficiency in your assessment. Additionally, routine maintenance is crucial for longevity. A pump that requires frequent repairs will drain resources over time.
Pumping systems should also align with your specific needs. Sometimes, a lower-cost pump may not handle your requirements effectively. This inconsistency leads to inefficiencies and increased costs later. Understanding the right balance is key. In the long run, investing wisely can yield significant savings.





We are here to help you with all your queries and concerns, just write to us using the below form and we will get back to you as soon as we can.