When it comes to managing water flow for various applications, selecting the right wet pump is a crucial decision that can significantly impact efficiency and performance. Wet pumps are specifically designed to handle water and other liquids, making them essential in a wide range of industries such as agriculture, construction, and wastewater management. Understanding the different types of wet pumps available and their specific functionalities can help you make informed choices that align with your unique water needs.
This guide delves into the factors you should consider when choosing a wet pump, including flow rate, compatibility with the liquid being pumped, and the specific operational conditions of your application. With the diverse options on the market, it is vital to not only assess the performance characteristics of each wet pump but also to evaluate cost-effectiveness and maintenance requirements. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of these elements, you can optimize your water management efforts and ensure reliable operation in even the most demanding environments.
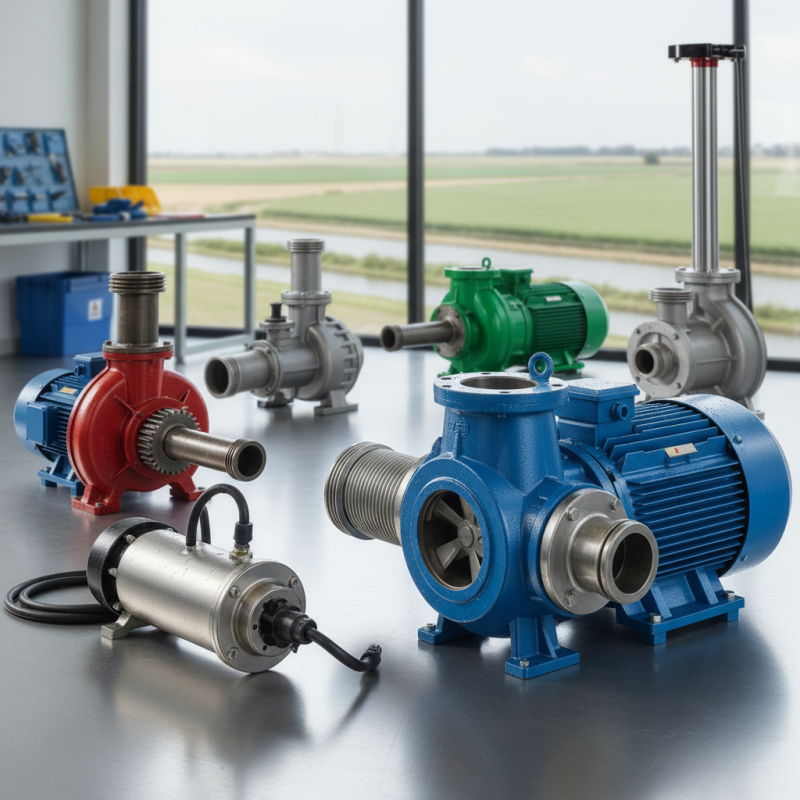

When selecting a wet pump, it's essential to understand the various types available to meet specific water needs. Wet pumps generally fall into categories such as submersible pumps, centrifugal pumps, and diaphragm pumps, each with distinct advantages and application areas. For example, the submersible pump, which operates submerged in the fluid it is pumping, is ideal for applications where space is limited, and it can handle up to 2,000 gallons per minute (GPM) efficiently. A study by the Hydraulic Institute notes that submersible pumps account for approximately 30% of the market due to their versatility in municipal water systems and sewage treatment plants.
Centrifugal pumps, on the other hand, utilize rotational energy to move fluid and are highly effective for moving large volumes of water. According to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, centrifugal pumps are preferable for applications requiring consistent flow rates, as they have efficiencies exceeding 85% in optimal conditions. Meanwhile, diaphragm pumps provide a unique solution for transferring viscous and abrasive fluids, making them suitable for agricultural or industrial applications. A report by Research and Markets highlights an increasing trend for diaphragm pumps, projecting a CAGR of 6.2% through 2028 as industries recognize their benefits in handling challenging fluids. Understanding these distinctions allows businesses to choose the right wet pump tailored to their operational requirements.
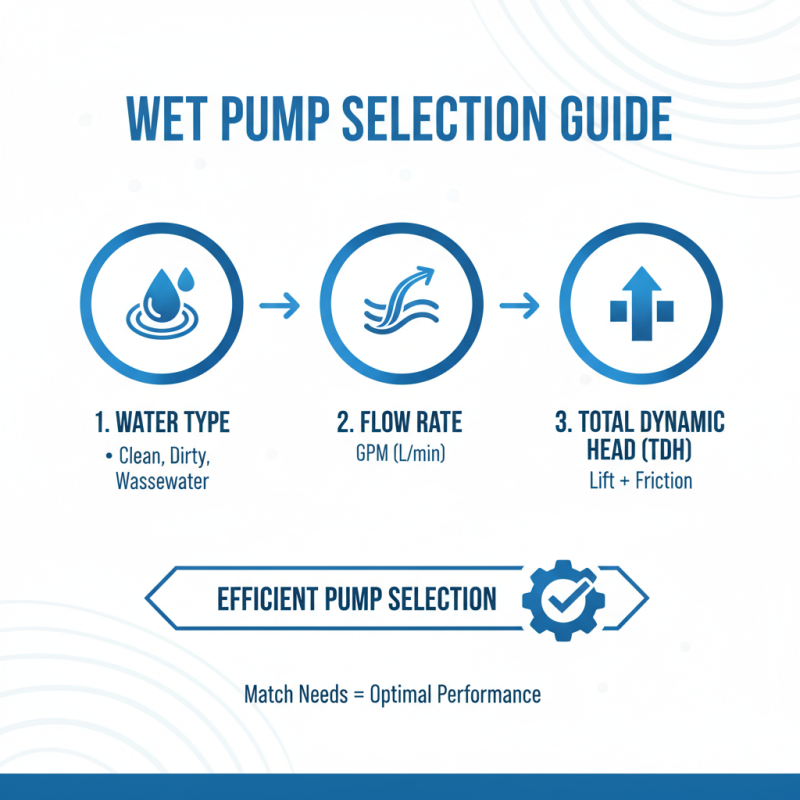
When selecting a wet pump, it’s essential to start with a clear understanding of your specific water needs. Consider factors such as the type of water you will be pumping (clean, dirty, or wastewater), the required flow rate, and the total dynamic head (TDH). Understanding these parameters will help you narrow down your options and choose a pump that can efficiently meet your requirements.
**Tips:** Assess your flow rate needs by measuring the volume of water you need to move and how quickly. If your projects involve dealing with dirty water, look for pumps designed to handle solids and debris without clogging. Additionally, don't overlook the importance of the material construction of the pump; it should be compatible with the type of water to ensure durability and reliability.
Another crucial aspect is the power source. Electric pumps are common, but if you need mobility or are working in locations without electricity, a gas-powered option might be preferable. Always verify the specifications against your specific applications to ensure optimal performance.
**Tips:** Investigate the energy efficiency of the pump models you consider to minimize long-term operational costs. Regular maintenance can also enhance the lifespan and efficiency of your pump, so consider the ease of serviceability in your selection process.
When selecting a wet pump, it is crucial to identify the specific features that will meet your water needs effectively. One key feature to consider is the pump's capacity, typically measured in gallons per minute (GPM). According to a report by the Hydraulic Institute, the optimum flow rate for residential applications usually falls between 10 to 30 GPM, depending on the size of the property and its water usage patterns. Understanding your required flow rate can significantly influence the performance and efficiency of your system.
Another important characteristic is the pump's horsepower (HP) rating. A higher HP ensures that the pump can handle more demanding tasks without overheating or breaking down. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) suggests selecting a pump with at least 1 HP for applications involving heavier water movement, such as draining basements or managing irrigation in larger fields. Additionally, examining the pump's materials and construction, such as corrosion-resistant options for harsh environments, will enhance durability and lifespan. By prioritizing these key features, you can make a well-informed decision tailored to your specific water needs.

When choosing a wet pump, it is crucial to evaluate three core performance metrics: flow rate, head pressure, and efficiency. The flow rate, typically measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per second (L/s), determines how much water the pump can deliver in a given timeframe. For instance, according to the Hydraulic Institute, a flow rate of 100 GPM is considered suitable for medium-sized residential applications, while larger commercial setups may require pumps that can handle upwards of 500 GPM. Understanding the required flow rate for your specific application will help you select a pump that meets your water delivery needs effectively.
Head pressure, measured in feet or meters, indicates how high a pump can raise water and is essential for systems where water must be lifted to a specific elevation. Many pumps offer a head pressure rating that helps assess their efficiency, particularly in applications like irrigation or drainage. The World Pump Industry Report states that pumps with a head pressure of at least 20 feet are often necessary for effective irrigation over significant distances. Lastly, efficiency should not be overlooked; a pump's efficiency rating affects its operational costs. According to data from the U.S. Department of Energy, electric motor-driven pumps can operate at efficiencies as low as 30% in poor designs while high-efficiency models can exceed 85%, significantly impacting energy usage and overall cost-effectiveness. Evaluating these performance metrics carefully ensures that you choose a wet pump tailored to your specific water needs.
When selecting a wet pump, keeping maintenance in mind is crucial for ensuring its longevity and efficient operation. First and foremost, regular inspection of the pump is essential. Look for any signs of wear, such as leaks or unusual noises. These early warnings can prevent more significant issues down the line.
Another useful tip is to keep the pump clean. Ensure that the intake screens and filters are free from debris, which can obstruct water flow and strain the pump. Regularly scheduled cleaning can significantly extend the life of your pump. Additionally, it's important to check and replace any worn-out seals or gaskets promptly to avoid unnecessary damage.
Lastly, consider the lubrication of moving parts. Using the right lubricant at recommended intervals can keep components running smoothly and reduce the risk of overheating. Maintaining a consistent schedule for lubrication will not only enhance performance but also enhance the durability of the wet pump, ensuring it meets your water needs efficiently over time.
| Pump Type | Ideal Use Case | Flow Rate (GPM) | Power Rating (HP) | Maintenance Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Submersible Pump | Draining water from basements | 30-50 | 0.5-2 | Every 6 months |
| Pedestal Pump | Sump pits, sewage applications | 20-40 | 0.5-1.5 | Annually |
| Drainage Pump | Emptying flooded areas | 50-100 | 1-4 | Every 3 months |
| Effluent Pump | Moving wastewater from septic systems | 10-30 | 0.5-2 | Every 6 months |
| Centrifugal Pump | Irrigation and agricultural use | 50-150 | 2-10 | Quarterly |





We are here to help you with all your queries and concerns, just write to us using the below form and we will get back to you as soon as we can.