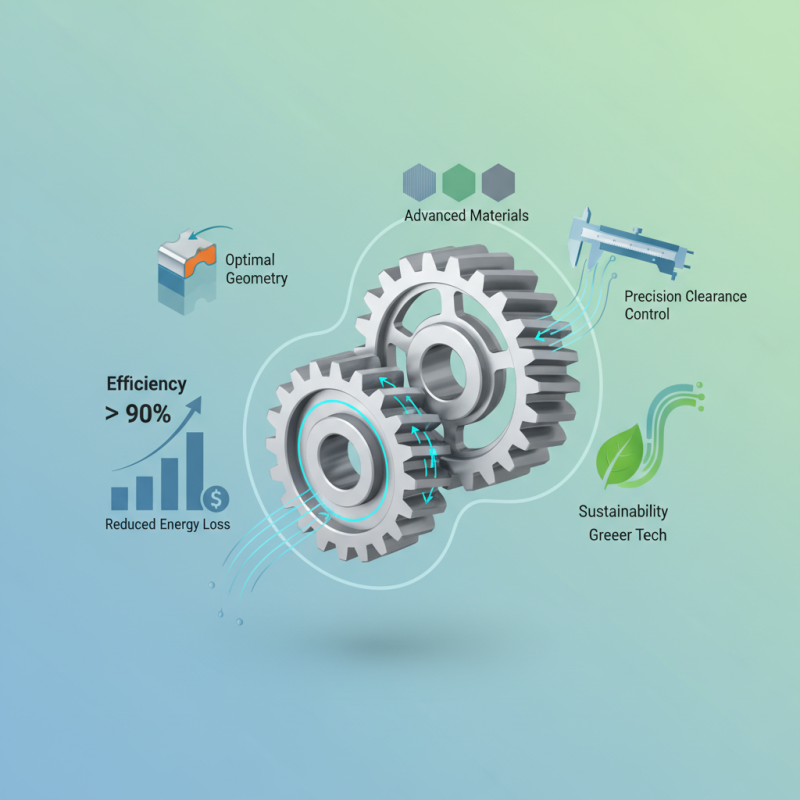
In the realm of fluid transfer and hydraulic systems, the design of gear pumps plays a crucial role in enhancing operational efficiency and performance. According to the Hydraulic Institute, gear pumps are capable of delivering flow rates that can range significantly, often achieving efficiencies of 90% or higher when optimally designed. As industries continue to seek cost-effective and reliable solutions, mastering the intricacies of gear pump design is essential for engineers and manufacturers alike.
Expert insights emphasize the importance of precision in gear pump design. Dr. Jane Holloway, a leading authority in hydraulic engineering, states, "A well-optimized gear pump not only boosts performance but also minimizes energy loss, which is vital for sustaining competitive advantage in the market." This highlights the necessity for engineers to focus on factors such as gear tooth geometry, material selection, and clearance control to achieve maximum efficiency.
Moreover, as sustainability becomes a paramount concern across all sectors, adopting advanced gear pump design methodologies is imperative. Enhancing design parameters can lead to reduced energy consumption and lower operational costs, aligning with the growing demand for greener technologies in fluid mechanics. By prioritizing innovative design approaches, industries can ensure that their gear pumps operate at peak performance while contributing to overall environmental stewardship.
Understanding the operation and design of gear pumps is crucial for optimizing their efficiency and performance across various industrial applications. Gear pumps operate based on the principle of positive displacement, where two or more gears rotate to transport fluid within the pump housing. This mechanism creates a sealed chamber in which the liquid is trapped and moved from the inlet to the outlet. According to a report by the Hydraulic Institute, optimizing gear design can lead to efficiency rates exceeding 90%, which is significant compared to other types of pumps. Key factors influencing this efficiency include gear geometry, material selection, and clearance within the casing.
When designing a gear pump, attention must be paid to the gear profile and size, as these elements directly impact the flow rate and pressure capabilities of the pump. Research suggests that a reduction in the side clearance between the gears can minimize leakage, thereby enhancing volumetric efficiency. Furthermore, adopting advanced materials can improve wear resistance and thrust balance, extending the life of the pump. A well-designed gear pump not only increases energy efficiency but also reduces operational costs, making it a valuable component in fluid transfer systems in sectors such as automotive and manufacturing. Data from the American Pump Manufacturers Association shows that properly designed gear pumps contribute to up to 30% lower energy consumption in hydraulic systems, showcasing the potential gains from meticulous design.

The efficiency and performance of a gear pump are significantly influenced by several key factors that must be meticulously considered during the design process. First and foremost, the gear profile, which typically includes the involute profile, plays a critical role in minimizing sliding friction between the gears. Reports indicate that optimizing the gear tooth design can enhance volumetric efficiency by approximately 5-10%. This optimization is essential as it directly impacts the flow rate and reduces energy losses, leading to improved overall performance.
Another crucial factor is the selection of materials used in gear construction. High-performance materials such as hardened steel or specialized composites can withstand higher loads and resist wear better than conventional materials. According to a study published by the Hydraulic Institute, using advanced materials can reduce wear rates by as much as 30%, thereby extending the operational lifespan of the pump while maintaining high efficiency. Additionally, the tolerance settings during manufacturing are vital; tighter tolerances lead to better sealing and reduced leakage, which are paramount for maximizing the efficiency of the pump operations.
Lastly, the operating environment, including temperature and viscosity of the fluid being pumped, can significantly impact performance. For instance, a viscosity increase can lead to higher torque requirements, effectively reducing efficiency by up to 15% if not properly accounted for in pump design. Therefore, understanding the interplay between these factors is essential in achieving maximum efficiency and performance in gear pump design.
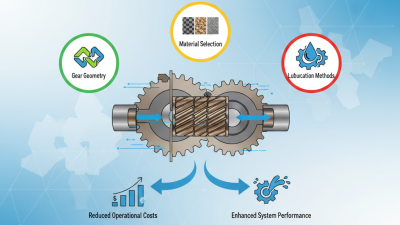
The selection of materials is crucial in the design of gear pumps, as it directly impacts their efficiency, durability, and performance. When choosing materials, engineers must consider factors such as viscosity, temperature range, and chemical compatibility. High-strength alloys are often preferred for the gears to ensure longevity and withstand aggressive operating conditions. Additionally, materials with low friction coefficients, such as certain polymers or treated metals, can significantly improve the pump’s efficiency by reducing energy losses during operation.
Another important aspect of material selection is the ability to resist wear and corrosion, especially in applications involving abrasive or corrosive fluids. Stainless steels and specialized coatings may be utilized to enhance the pump’s resistance to these damaging effects. Furthermore, the housing and sealing materials should be chosen to maintain structural integrity while preventing leaks. This comprehensive approach to material selection not only optimizes gear pump performance but also minimizes maintenance needs, ensuring consistent and reliable operation over time.
The precision engineering of gear tooth design is crucial in maximizing the efficiency and performance of a gear pump. Gear teeth must be meticulously crafted to ensure optimal meshing, which directly influences the pump's ability to transfer fluids effectively. Accurate tooth geometry, including profile curvature and spacing, minimizes friction and wear, thus enhancing the pump's operational lifespan. Advanced computer-aided design tools allow engineers to simulate various tooth configurations, enabling them to identify the most efficient designs well before physical prototyping.
In addition to geometry, the materials used in gear tooth construction play a significant role in performance. Selecting high-quality materials that can withstand the stresses and strains during operation is essential. Treatments such as hardening and surface finishing can further boost durability and reduce the likelihood of failure. By focusing on precision during the design phase, engineers can create gear pumps that not only operate more efficiently under variable loads but also maintain consistent performance in diverse applications, ranging from hydraulic systems to automotive uses. This level of precise engineering ultimately reduces energy consumption and enhances the overall reliability of the pump.
Testing and validation play a crucial role in optimizing the efficiency of gear pumps. To ensure that a gear pump is operating at peak performance, various testing methods can be employed, such as flow rate analysis, pressure testing, and thermal efficiency assessments. These tests not only help identify areas for improvement but also establish baseline metrics that inform future designs. By simulating different operating conditions, engineers can determine the pump's response to changes in viscosity, temperature, and pressure, which are critical factors influencing performance.
In addition to standard testing procedures, advanced techniques such as computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations can provide deeper insights into fluid behavior within the pump. By analyzing how the fluid moves through the gears and around the pump casing, engineers can fine-tune design parameters to minimize losses caused by turbulence and friction. Validating these findings with physical prototypes allows for a comprehensive evaluation of design effectiveness, ensuring that adjustments lead to measurable improvements in efficiency and reliability. Through rigorous testing and validation, the overall performance of gear pumps can be significantly enhanced, leading to better operational outcomes in various applications.




We are here to help you with all your queries and concerns, just write to us using the below form and we will get back to you as soon as we can.