When it comes to machinery and vehicles, the efficiency of performance crucially hinges on the type of lubricants used. Among these essential fluids, oil for gear stands out as a vital component for ensuring smooth operation and longevity of gear systems. Gear oil is specifically formulated to withstand the extreme conditions that gears endure, including high pressure, varying temperatures, and the inherent friction that occurs during motion. Understanding the different types of gear oils available and their unique properties is key to selecting the right lubricant for specific applications.
In this guide, we will delve into the world of gear oil, exploring its various types, including synthetic and mineral options, as well as how each type contributes to the optimal performance of gears in different settings. Whether in automotive applications, industrial machinery, or any mechanical gearbox, the correct choice of oil for gear can make a substantial difference in performance, efficiency, and gear life. By recognizing the critical role that gear oil plays, users can make informed decisions that enhance the functionality and durability of their equipment.

Gear oil is a specialized lubricant designed to reduce friction and wear in gear systems, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of machinery. Its primary function is to provide a protective barrier between moving metal surfaces, which is crucial in gear assemblies that operate under heavy loads and varying speed conditions. The formulation of gear oil typically includes base oils and various additives that enhance its protective properties, including anti-wear, rust prevention, and thermal stability.
The importance of gear oil in machinery cannot be overstated. It not only facilitates smoother operation of gears but also mitigates overheating by dissipating heat generated during gear interactions. In addition, high-quality gear oil helps prevent corrosion and prolongs the lifespan of critical components, thereby reducing maintenance costs and downtime. Understanding the types of gear oils available and their specific applications enables operators to select the appropriate lubricant, ensuring that their machinery operates efficiently and effectively, even in demanding environments.
Gear oil is essential for the efficient operation of mechanical systems, particularly those involving gears and bearings. Understanding the various types of gear oil available is crucial for maintaining optimal performance, as each type is formulated to meet different requirements based on application, temperature, and load conditions.
There are several key variants of gear oil, including mineral-based, synthetic, and semi-synthetic oils. Mineral-based gear oils are derived from refining crude oil and are commonly used due to their good lubrication properties and affordability. Synthetic gear oils, on the other hand, are engineered for superior performance in extreme temperatures and high loads, often offering enhanced protection and reduced wear. Semi-synthetic oils combine the benefits of both mineral and synthetic oils, providing a balanced option for many applications.
Additionally, gear oils can be categorized by their viscosity ratings, commonly known as the "weight" of the oil. For instance, multi-grade oils are designed to perform well under varying temperatures, ensuring proper lubrication whether the system is cold-starting or operating at high temperatures. Understanding these types of gear oil allows for informed decisions that can significantly enhance the longevity and efficiency of machinery and automotive systems.
Gear oil is essential in various industries and vehicles, offering lubrication and protection for different types of gear systems. In automotive applications, gear oil is crucial for manual transmissions and differential gears, ensuring smooth shifting and minimizing wear. The formulation of gear oil can vary, typically designed to withstand high pressure and manage heat generated during operation. This is particularly important in high-performance vehicles where maintaining optimal performance is critical.
In industrial settings, gear oil plays a significant role in the operation of machinery and equipment. It is used in gearboxes, hydraulic systems, and other mechanical components to ensure reliability and efficiency. Different industries, such as manufacturing, mining, and construction, rely on specific types of gear oil tailored to their operational demands. For instance, heavy machinery may require gear oils with extreme pressure additives to handle the immense loads and stress the equipment experiences during operations. By understanding the specific applications and types of gear oil, industries can enhance equipment longevity and performance.
Gear oil plays a crucial role in the performance and longevity of machinery, particularly in automotive and industrial applications. Understanding the properties of gear oil, such as viscosity, additives, and overall performance, is essential for optimal functionality.
Viscosity, which measures a fluid's resistance to flow, is a key factor. It ensures that the oil can adequately lubricate gears under various operating temperatures. The right viscosity helps reduce wear and tear, preventing the gears from overheating and extending their service life.
In addition to viscosity, the presence of additives in gear oil enhances its protective qualities. Additives like anti-wear agents, rust inhibitors, and extreme pressure additives improve the oil's performance under heavy loads and harsh conditions. These chemical enhancements provide better protection against metal-to-metal contact, resulting in smoother operation and greater efficiency.
By selecting gear oils with the appropriate viscosity and additive package, users can ensure that their machinery operates optimally, even in demanding environments. Understanding these properties can significantly impact the maintenance and functionality of gear systems.
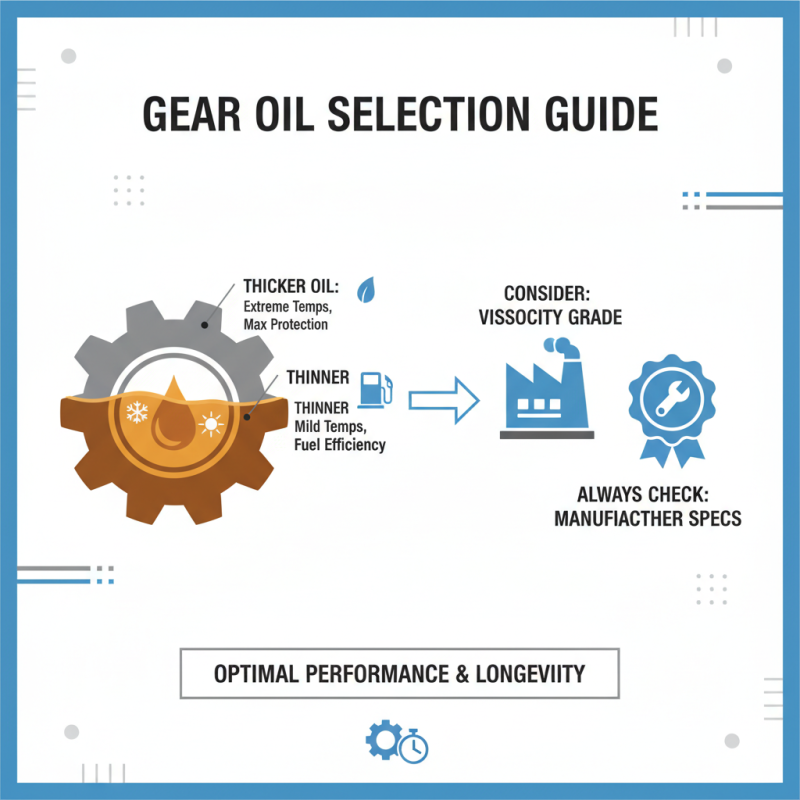
Selecting the right gear oil is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your machinery. When choosing gear oil, first consider the viscosity grade, which indicates how well the oil will perform at various temperatures. Thicker oils offer better protection in extreme temperatures, while thinner oils enhance fuel efficiency in milder conditions. Always refer to the manufacturer's recommendations to determine the appropriate viscosity for your specific application.
Next, pay attention to the oil’s additive package, which can significantly influence performance. Look for oils that contain additives designed to reduce friction, enhance lubrication, and prevent oxidation. For applications that experience high loads or extreme pressure, extreme pressure (EP) additives are essential to prevent metal-to-metal contact and extend the life of the gear components. Additionally, consider the environment where the oil will be used; for instance, if exposed to water or contaminants, select a gear oil with superior water resistance properties to ensure reliable operation.






We are here to help you with all your queries and concerns, just write to us using the below form and we will get back to you as soon as we can.