In the intricate world of hydraulic systems, the significance of gear pump design cannot be overstated. These pumps play a vital role in transferring fluid through various applications, ranging from industrial machinery to automotive systems. Renowned expert in hydraulic technologies, Dr. Emily Carter, has emphasized the importance of precision in this field, stating, "The efficiency and reliability of a hydraulic system highly depend on how well the gear pump is designed." Her insights shed light on the critical elements that engineers and designers must consider when developing gear pumps.
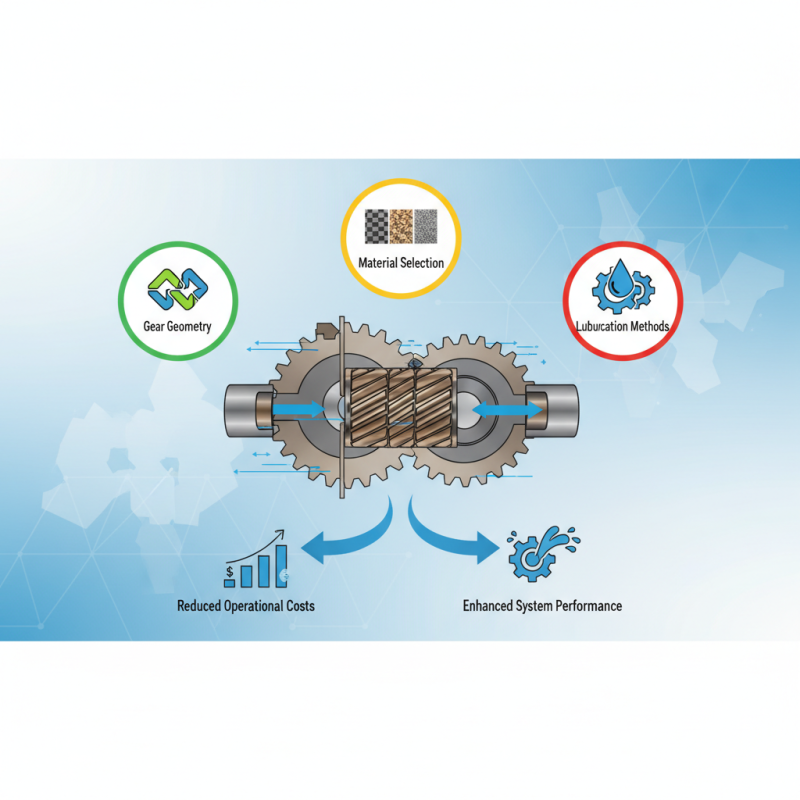
Understanding the fundamental principles of gear pump design is essential for optimizing performance and ensuring longevity. Key considerations include gear geometry, material selection, and lubrication methods, all of which can dramatically affect the pump’s efficiency. Moreover, best practices in design can lead to reduced operational costs and enhanced system performance, making it imperative for designers to stay informed about the latest advancements and techniques in the industry.
As we delve deeper into the nuances of gear pump design, we will explore various factors that impact functionality and reliability. By adhering to established best practices and understanding the underlying principles, engineers can create gear pumps that not only meet but exceed the demands of modern applications, ultimately driving innovation in the fluid power sector.
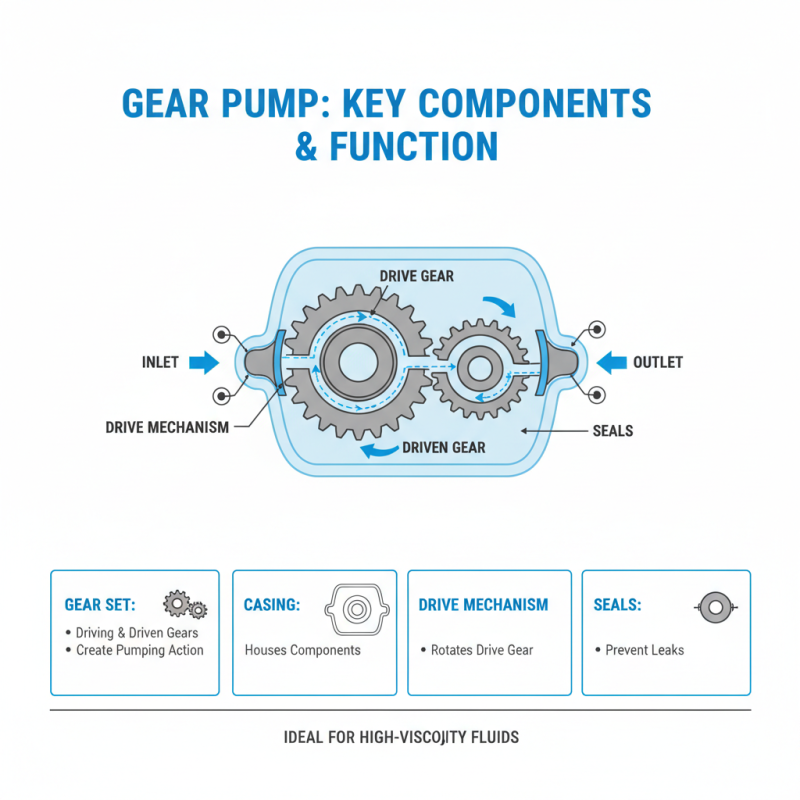
Gear pumps are essential components in various industrial applications, particularly for moving fluids with high viscosity. Understanding the key components of gear pumps is vital for optimizing their performance and longevity. The primary components include the gear set, casing, drive mechanism, and seals. The gear set, which includes both the driving and driven gears, is responsible for creating the pumping action. As the gears rotate, they trap fluid in the spaces between the teeth and transport it from the inlet to the outlet, a process that is influenced by the gear's design and material.
The casing serves as the outer shell of the pump, providing structural integrity and preventing leaks. Additionally, the drive mechanism is crucial as it converts rotational energy from a motor into mechanical force that drives the gears. According to a report by the International Pump Users’ Association, gear pumps have shown a 25% efficiency increase in various applications when compared to older models, highlighting the importance of high-quality materials and precision engineering in design.
Tip: When selecting gear pumps for specific applications, always consider the compatibility of materials with the fluid being pumped. Using incompatible materials can lead to degradation and pump failure.
Seals are another important component, preventing leakage and ensuring efficiency. Wear and tear in seals can drastically affect the performance of a gear pump; reports indicate that up to 70% of pump failures are linked to seal issues. Regular inspection and replacement of seals can significantly extend a pump’s operational lifetime.
Tip: Implement a routine maintenance schedule to check and replace worn seals, ensuring optimal performance and reducing the risk of costly downtime.
Gear pumps are widely recognized for their efficiency and reliability in fluid transfer applications. Understanding the different types of gear pumps is crucial for selecting the right pump for specific tasks. The two primary types are external gear pumps and internal gear pumps, with each serving distinct purposes based on their design and operational characteristics. External gear pumps are characterized by two intermeshing gears that create a sealed cavity, making them ideal for high-pressure applications such as hydraulic systems and fuel oil transfer. According to a report by Global Industry Analysts, the global external gear pump market is projected to reach USD 1.1 billion by 2026, highlighting the increasing demand in sectors like oil and gas and wastewater treatment.
On the other hand, internal gear pumps consist of a rotating gear inside a larger stationary gear, allowing for a more compact design and smoother operation, particularly with viscous fluids. This type is often used in applications requiring precise metering and low shear, such as in food processing and chemical industries. Market analysis indicates that internal gear pumps are gaining traction, with an anticipated growth rate of 5.2% annually through 2025, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies and applications in various sectors including pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. Understanding these differences aids industries in optimizing their operations by selecting the most appropriate gear pump type to match their specific fluid characteristics and operational demands.
When designing gear pumps for optimal efficiency, it is essential to focus on several key considerations that directly impact performance and longevity. One of the foremost aspects is the selection of materials for both the gears and the casing. A report by the Hydraulic Institute indicates that using high-quality materials can enhance durability and reduce wear, which is critical in high-pressure applications. For instance, stainless steel offers excellent resistance to corrosion while maintaining strength, making it ideal for various fluid pumping applications. Proper material selection not only affects the pump's lifespan but also its efficiency, with some studies suggesting an improvement in volumetric efficiency by up to 5% when utilizing advanced materials.
Another crucial design consideration is the precision of gear meshing. Accurate alignment and minimal tolerances between gears can significantly reduce hydraulic losses. According to a study published in the Journal of Fluid Engineering, optimizing the gear tooth profile can increase efficiency ratings substantially. Furthermore, incorporating features like pressure relief valves and suitable sealing materials can minimize leakage and ensure consistent operation under varying load conditions. As reported in market analysis by Research and Markets, enhancing pump design to focus on these details can lead to operational improvements, including a reduction in energy consumption by up to 15%, positively impacting overall system efficiency. By prioritizing these design elements, engineers can ensure that gear pumps operate reliably and efficiently across a range of applications.
When designing gear pumps, engineers often face a myriad of challenges that can complicate the manufacturing and efficiency of the final product. One common issue is the proper selection of materials, which directly affects durability and performance. According to a report by the Hydraulic Institute, nearly 30% of premature pump failures are attributed to inadequate material selection. Utilizing advanced composites and high-strength alloys can significantly enhance the longevity and efficiency of gear pumps, mitigating risks associated with wear and fatigue.
Another challenge arises from the precise alignment and assembly of the gears. Misalignment can lead to increased friction, reduced efficiency, and ultimately, pump failure. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) emphasizes that achieving optimal alignment can boost pump performance by up to 15%. To overcome these obstacles, employing advanced manufacturing techniques such as CNC machining can ensure more accurate tolerances, thus enhancing the reliability of gear pumps.
Lastly, fluid dynamics play a crucial role in gear pump performance, with improper design leading to cavitation and flow disruptions. Industry research indicates that optimizing the hydrodynamic profile can reduce cavitation risk by as much as 25%. Implementing simulation tools during the design phase allows engineers to predict flow patterns and make necessary adjustments, leading to improved efficiency and a lower risk of operational issues. By addressing these common challenges with targeted solutions, designers can create more reliable and efficient gear pumps that meet the demands of various industrial applications.
When it comes to maintaining gear pumps, attention to detail is vital for ensuring reliability and optimal performance. According to a report from the Hydraulic Institute, approximately 60% of all pump failures are attributed to improper maintenance practices. This statistic highlights the necessity for robust maintenance protocols that encompass regular inspections, lubrication, and monitoring of operating conditions. Proper lubrication not only reduces friction but also prevents overheating—a common cause of pump failure. It is essential to choose the right type and amount of lubricant based on the operating environment and pump specifications.
Another critical aspect of gear pump reliability is condition monitoring. Utilizing advanced diagnostic tools, such as vibration analysis and thermal imaging, can provide early warnings of potential issues before they escalate into significant failures. The American Society for Mechanical Engineers has shown that implementing a predictive maintenance strategy can increase the lifespan of gear pumps by up to 30%. By routinely analyzing parameters like flow rates, pressure levels, and temperature, operators can identify abnormal trends and address them proactively. Thus, investing in a comprehensive maintenance program not only enhances pump reliability but also contributes to the overall efficiency of fluid handling systems.





We are here to help you with all your queries and concerns, just write to us using the below form and we will get back to you as soon as we can.