When it comes to selecting the perfect water pump for your needs, understanding the various types available on the market is crucial. The right water pump can significantly impact efficiency, performance, and longevity, whether you require it for irrigation, household use, or industrial applications. With a myriad of options to choose from, including centrifugal, submersible, and diaphragm pumps, the decision can feel overwhelming. This guide aims to simplify the process by providing an overview of the top water pump types, their specific features, and applications.
Moreover, considerations such as flow rate, head pressure, and energy efficiency play a vital role in your selection process. By comprehensively examining these aspects, you can ensure that your chosen water pump will meet the demands of your particular project or facility. Our guide not only details the key characteristics of each pump type but also offers practical tips on how to evaluate which water pump is best suited for your needs. Join us as we navigate through the essential factors to consider, ensuring that you make an informed decision for your water pumping requirements.
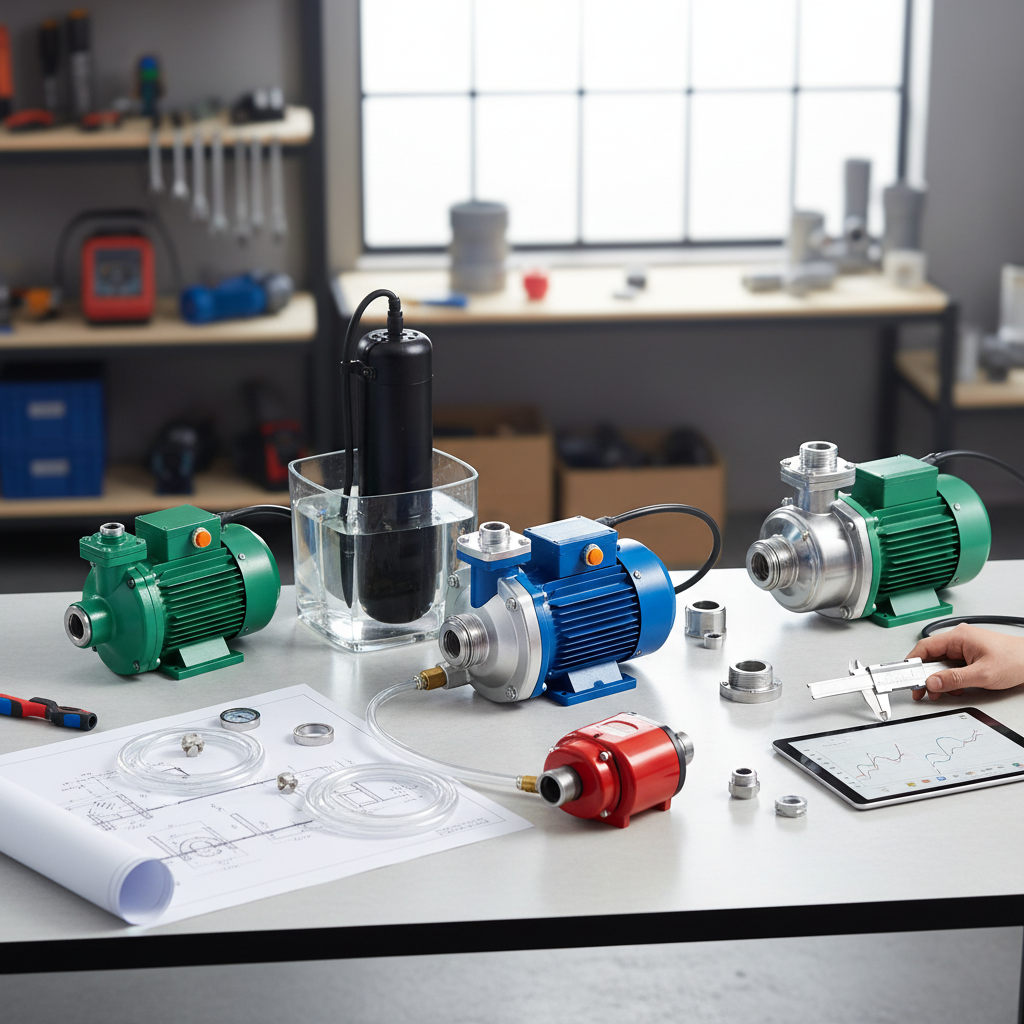

When selecting the best water pump for your needs, it's crucial to understand the various types available in the market. The most common varieties include centrifugal pumps, submersible pumps, and positive displacement pumps. According to the Global Water Pump Market Report, the centrifugal pump segment is projected to dominate the market, accounting for nearly 50% of total share by 2025, owing to its efficiency in transporting fluids in industrial applications.
Centrifugal pumps are ideal for applications requiring high flow rates and low pressure, such as irrigation and water supply systems. Conversely, submersible pumps, which operate while submerged in liquid, are often utilized in drainage, sewage, and deep well applications. The increasing need for efficient wastewater management is expected to drive the submersible pump market, with anticipated growth rates of over 6% annually between 2023 and 2025. Positive displacement pumps, though less common, are vital in circumstances needing precise flow control, making them essential in industries like oil and gas.
Understanding these categories is essential for making an informed decision. Each pump type serves distinct purposes, and choosing the right one can enhance operational efficiency and reduce overall costs, aligning with market trends and technological advancements outlined in the latest industry analysis.
When selecting the right water pump for your specific application, it’s crucial to understand the key criteria that dictate performance and efficiency. First, assess the flow rate required for your task. This measurement, typically expressed in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per second (L/s), should align with your operational needs. For example, a garden irrigation system may require a pump with a higher flow rate than a small fountain.
Another important aspect to consider is the pump's head pressure, which refers to the height a pump can elevate water. This is vital for applications such as drip irrigation or water transport across varying elevations. Additionally, energy efficiency is critical; selecting a pump with a suitable horsepower rating can help minimize operational costs while ensuring adequate performance.
Tips: Before making your final decision, evaluate the pump materials as well. Choosing corrosion-resistant materials can ensure longevity, especially in environments where water chemistry may affect pump integrity. Also, consider purchasing pumps from reputable brands that offer warranties and customer support, as this can provide peace of mind during usage. Finally, always read reviews from other users to gauge reliability and ease of use, helping you make a well-informed choice.

When selecting the right water pump for your needs, understanding flow rate and head is crucial. Flow rate, measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per second (L/s), indicates the volume of water a pump can move within a specified time. According to the American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, home irrigation systems typically require flow rates ranging from 5 to 20 GPM, depending on the size of the system and the types of plants being watered. For instance, a small garden may only need a pump with a flow rate of 8 GPM, while a larger landscape might require up to 20 GPM to adequately supply water.
Head, on the other hand, refers to the height water can be lifted by the pump, measured in feet or meters. It is essential to consider both total dynamic head (TDH) and static head, as TDH encompasses the energy losses caused by friction and other factors in the system. A report from the Hydraulic Institute indicates that most residential applications require a head ranging from 20 to 60 feet. Underestimating the required head can lead to inadequate water pressure, resulting in inefficient operation and potential damage to your irrigation system. By adequately assessing both flow rate and head, you can ensure optimal performance and longevity of your water pump.
When selecting a water pump, energy efficiency should be a primary consideration, as it directly affects both operational costs and environmental impact. Modern water pumps are available in a variety of designs, some of which incorporate advanced technologies that enhance their efficiency. Look for pumps that have high-efficiency motors or variable frequency drives (VFDs). These features allow the pump to adjust its speed based on demand, reducing unnecessary energy consumption during periods of low water usage.
Additionally, the pump's application can influence its energy efficiency. For instance, centrifugal pumps are ideal for high-flow, low-pressure applications, while positive displacement pumps work better in scenarios requiring high pressure. Compare the performance curves of different models to identify the most energy-efficient option for your specific needs. By making an informed choice about the right type of water pump and its energy requirements, you can significantly reduce electricity usage, lower operational costs, and contribute to sustainable water management practices.
| Pump Type | Flow Rate (GPM) | Head Height (ft) | Power Rating (HP) | Energy Efficiency Rating (EER) | Estimated Annual Energy Cost ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Submersible Pump | 30 | 25 | 1.5 | 4.0 | 200 |
| Jet Pump | 20 | 30 | 1.0 | 3.5 | 180 |
| Centrifugal Pump | 50 | 15 | 2.0 | 4.5 | 220 |
| Diaphragm Pump | 15 | 10 | 0.5 | 3.0 | 160 |
| Submersible Sump Pump | 25 | 12 | 0.75 | 3.8 | 175 |
Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of a water pump. According to data from the American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers (ASABE), regular maintenance can extend a pump's lifespan by up to 30%. This involves routine inspections, cleaning, and timely replacement of worn-out parts. For instance, checking the seals and bearings can prevent leaks and reduce friction, which are common causes of pump failure. Additionally, maintaining optimal fluid levels and monitoring the pump's operating conditions can significantly enhance its performance.
Furthermore, the Water Systems Council emphasizes that proactive maintenance not only prolongs a pump's operational life but also promotes efficiency. A water pump operating at peak efficiency can save up to 20% on energy costs. Users should follow manufacturer guidelines for maintenance intervals and keep comprehensive records of service and repairs. By implementing these practices, water pump owners can ensure their systems remain reliable, avoiding costly replacements and downtime in the long run.






We are here to help you with all your queries and concerns, just write to us using the below form and we will get back to you as soon as we can.