Water with pump is a fascinating concept that plays a vital role in our daily lives. It refers to the process of using a pump to move water from one place to another. This technology is crucial for various applications, from irrigation in agriculture to supplying water in urban areas.
Understanding how water with pump functions helps us appreciate its significance. A pump draws water from a source and propels it through pipes. This movement enables efficient distribution, ensuring that homes and businesses have access to clean water. However, it’s essential to consider the limitations and potential failures of these systems. Poor maintenance or malfunctioning equipment can lead to water shortages or contamination.
As we delve deeper into the workings of water with pump, we can explore innovative designs and solutions. Reflecting on past challenges may inspire future improvements. Water accessibility is essential for health and sustainability, and grasping this technology opens up discussions on better management practices.

Water with pump systems play a crucial role in various industries, including agriculture and construction. These systems efficiently move water from one location to another, ensuring a reliable supply for irrigation and other processes. According to a report by the World Health Organization, over 2 billion people lack access to safe drinking water, making effective water pumping systems essential.
In agricultural settings, the use of pumps can significantly boost productivity. A study indicates that drip irrigation systems can reduce water usage by up to 70% compared to traditional methods. However, many farmers struggle with maintaining their pumps, leading to inefficiencies. Regular maintenance and monitoring are often overlooked, which can result in increased operational costs and decreased efficiency.
Pumps can also be found in urban infrastructure, such as wastewater treatment plants. The Environmental Protection Agency reports that about 850 billion gallons of wastewater are treated each year in the U.S. alone. However, only a fraction of these systems operate at optimal efficiency. Issues like clogging and outdated technology can hinder performance and contribute to environmental problems. Addressing these challenges could enhance both water management and sustainability efforts in communities worldwide.
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Water Source | Natural sources such as rivers, lakes, and groundwater. |
| Pump Type | Types include centrifugal, submersible, and diaphragm pumps. |
| Flow Rate | Measured in liters per minute (L/min), varying based on the pump type and application. |
| Uses | Irrigation, drinking water supply, industrial processes, and aquariums. |
| Energy Source | Electricity, gasoline, or solar energy can power pumps. |
| Maintenance | Regular checks on seals, filters, and impellers to ensure efficiency. |
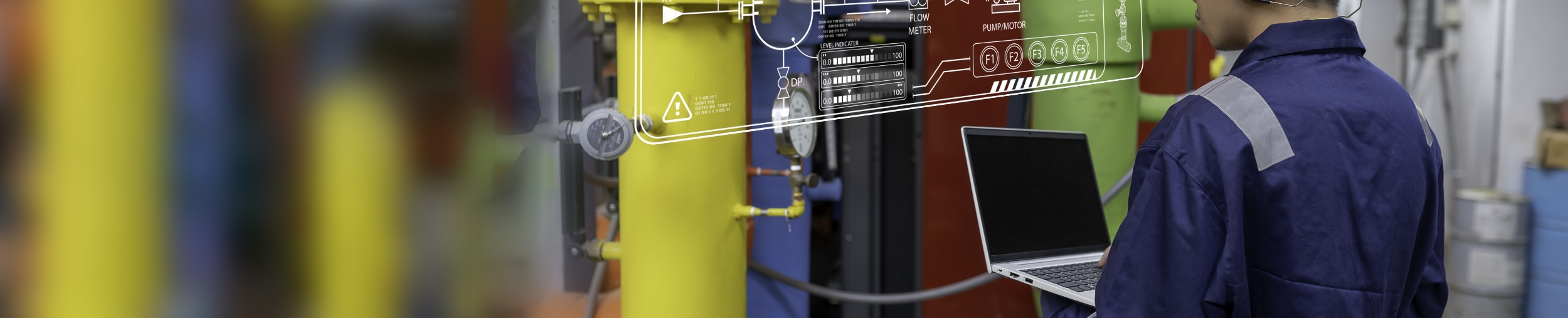
A water pump system consists of several key components. The motor provides power, driving the pump. It can be electric or powered by another energy source. Next, there's the pump itself, which draws water from a source and moves it through pipes. The efficiency of the pump can vary based on design. Common types include centrifugal and positive displacement pumps.
Piping is also crucial in this system. It connects the pump to the water source and the destination. Poorly installed pipes may cause leaks or pressure drops. A controller manages the flow and pressure, ensuring smooth operation. Many systems use sensors to monitor these aspects. However, these can sometimes fail, leading to malfunctions.
Storage tanks often store the pumped water for later use. They help maintain pressure and ensure a steady supply. If a tank is too small, it may lead to shortages. Valves are necessary for controlling the flow and directing water as needed. Each component plays a role, but issues can arise if not properly maintained or installed. Regular checks can help identify problems before they escalate.
Water pumps are vital for moving water in various settings. Understanding how they operate can simplify tasks that seem complicated. A water pump works by creating a difference in pressure. This mechanism draws water from one place and pushes it to another.
The process starts when the pump is activated. It draws water into an inlet. Then, an impeller or diaphragm transfers the water. This push creates flow and causes water to exit the outlet. Many pumps create suction to lift water from wells or reservoirs. Sometimes, it feels like magic when the water flows rapidly, but it's all about physics and mechanics.
Problems can arise during operation. Clogs can halt the movement of water. If the pump isn’t sized correctly, it may overheat or perform poorly. It’s essential to regularly inspect and maintain pumps. An overlooked issue can lead to costly repairs. Understanding these basic operations helps users make better decisions and avoid potential headaches.
This chart illustrates the efficiency of different types of water pumps as a percentage. Higher efficiency indicates better operation and performance, essential for effective water management in various applications.

Water pumps are crucial across various industries, providing the necessary flow for numerous applications. There are several common types of water pumps, each designed for specific tasks. For instance, centrifugal pumps, which dominate the market, are widely used in agriculture and construction. They can move water quickly and efficiently, making them ideal for irrigation.
Submersible pumps are another common type. These pumps operate underwater and are popular for draining wells or flooded areas. According to the Hydraulic Institute, submersible pumps can be up to 70% more efficient than other surface pumps in certain applications. This efficiency can greatly reduce operational costs but requires regular maintenance.
Additionally, positive displacement pumps are known for their ability to handle viscous fluids, widely used in industrial settings. They ensure a consistent flow rate, making them favorable in certain manufacturing processes. However, these pumps might need more frequent repairs due to the nature of their operation. The decision on which pump to use often involves a complicated analysis of costs, maintenance, and application needs. Clarity around these choices could be improved in many sectors, highlighting the need for better industry education.

Maintaining your water pump is crucial for longevity and efficiency. Regular checks can prevent larger problems later. Inspect hoses and connectors for any leaks or wear. It's surprising how a small issue can escalate quickly. Clean the filters on a routine basis. Dirty filters restrict flow and can hinder performance.
Monitoring the pump’s pressure is essential. Low pressure might indicate blockages or an issue with the motor. It’s not always easy to catch these problems early. Pay attention to unusual sounds as well. A grinding or rattling noise can signal underlying issues. Don't ignore these signs; they can lead to costly repairs.
Lastly, consider the installation location. Ensure it’s well-ventilated and protected from extreme weather. A little foresight can save a lot of headaches. Sometimes, people overlook seasonal maintenance. They wait until something goes wrong, which is never ideal. Regular upkeep helps ensure your pump runs smoothly and efficiently. It’s a task that requires some effort, but the benefits are well worth it.





We are here to help you with all your queries and concerns, just write to us using the below form and we will get back to you as soon as we can.